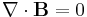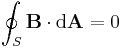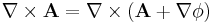Gauss's law for magnetism
| Electromagnetism |
|---|
|
In physics, Gauss's law for magnetism is one of Maxwell's equations, the four equations that underlie classical electrodynamics. It states that the magnetic field B has divergence equal to zero[1], in other words, that it is a solenoidal vector field. It is equivalent to the statement that magnetic monopoles do not exist. Rather than "magnetic charges", the basic entity for magnetism is the magnetic dipole. (Of course, if monopoles were ever found, the law would have to be modified, as elaborated below.)
Gauss's law for magnetism can be written in two forms, a differential form and an integral form. These forms are equivalent due to the divergence theorem.
The name "Gauss's law for magnetism"[1] is not universally used. The law is also called "Absence of free magnetic poles".[2] (or some variant); one reference even explicitly says the law has "no name".[3] It is also referred to as the "transversality requirement"[4] because for plane waves it requires that the polarization be transverse to the direction of propagation.
Contents |
Differential form
The differential form for Gauss's law for magnetism is the following:
where
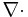 denotes divergence,
denotes divergence,- B is the magnetic field.
Integral form
The integral form of Gauss's law for magnetism states:
where
- S is any closed surface (a "closed surface" is the boundary of some three-dimensional volume; the surface of a sphere or cube is a "closed surface", but a disk is not),
- dA is a vector, whose magnitude is the area of an infinitesimal piece of the surface S, and whose direction is the outward-pointing surface normal (see surface integral for more details).
The left-hand side of this equation is called the net flux of the magnetic field out of the surface, and Gauss's law for magnetism states that it is always zero.
The integral and differential forms of Gauss's law for magnetism are mathematically equivalent, due to the divergence theorem. That said, one or the other might be more convenient to use in a particular computation.
The law in this form states that for each volume element in space, there are exactly the same number of "magnetic field lines" entering and exiting the volume. No total "magnetic charge" can build up in any point in space. For example, the south pole of the magnet is exactly as strong as the north pole, and free-floating south poles without accompanying north poles (magnetic monopoles) are not allowed. In contrast, this is not true for other fields such as electric fields or gravitational fields, where total electric charge or mass can build up in a volume of space.
In terms of vector potential
Due to the Helmholtz decomposition theorem, Gauss's law for magnetism is equivalent to the following statement:[5][6]
- There exists a vector field A such that

The vector field 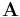 is called the magnetic vector potential.
is called the magnetic vector potential.
Note that there is more than one possible A which satisfies this equation for a given B field. In fact, there are infinitely many: Any field of the form 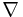 φ can be added onto A to get an alternative choice for A, by the identity (see Vector calculus identities):
φ can be added onto A to get an alternative choice for A, by the identity (see Vector calculus identities):
This arbitrariness in A is called gauge freedom.
In terms of field lines
The magnetic field B, like any vector field, can be depicted via field lines (also called flux lines)-- that is, a set of curves whose direction corresponds to the direction of B, and whose areal density is proportional to the magnitude of B. Gauss's law for magnetism is equivalent to the statement that the field lines have neither a beginning nor an end: Each one either forms a closed loop, winds around forever without ever quite joining back up to itself exactly, or extends to infinity.
Modification if magnetic monopoles exist
If magnetic monopoles were ever discovered to exist, then Gauss's law for magnetism would be disproved. Instead, the divergence of B would be proportional to the "magnetic charge density" 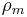 , as follows:
, as follows:
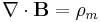 (SI units, weber convention)[7]
(SI units, weber convention)[7]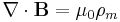 (SI units, ampere·meter convention)[8]
(SI units, ampere·meter convention)[8]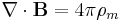 (cgs units)[9] where
(cgs units)[9] where 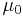 is the vacuum permeability.
is the vacuum permeability.
So far, despite extensive search no magnetic monopoles have been found.
History
The equation  was one of Maxwell's original eight equations. However, the interpretation was somewhat different: Maxwell's A field directly corresponded to an important physical quantity which he believed corresponded to Faraday's electrotonic state,[10] while the modern interpretation emphasizes gauge freedom, the idea that there are many possible A fields, all equally valid.[10]
was one of Maxwell's original eight equations. However, the interpretation was somewhat different: Maxwell's A field directly corresponded to an important physical quantity which he believed corresponded to Faraday's electrotonic state,[10] while the modern interpretation emphasizes gauge freedom, the idea that there are many possible A fields, all equally valid.[10]
See also
| Book: Maxwell's equations | |
| Wikipedia books are collections of articles that can be downloaded or ordered in print. | |
Notes
- ^ a b Tai L. Chow (2006). Electromagnetic Theory: A modern perspective. Jones and Bartlett. p. 134. ISBN 0-7637-3827-1. http://books.google.com/books?id=dpnpMhw1zo8C&pg=PA153&dq=isbn:0763738271#PPA134,M1.
- ^ John David Jackson (1999). Classical Electrodynamics (3rd ed.). Wiley. p. 237. ISBN 0-471-30932-X.
- ^ David J. Griffiths (1998). Introduction to Electrodynamics (3rd ed.). Prentice Hall. p. 321. ISBN 0-13-805326-X.
- ^ John D. Joannopoulos, Steve G. Johnson, Joshua N. Winn, Robert D. Meade (2008). Photonic Crystals: Molding the Flow of Light (2nd ed.). Princeton University Press. p. 9. ISBN 978-0-691-12456-8.
- ^ W.H.A. Schilders et al. (2005-05-23). Handbook of Numerical Analysis. p. 13. ISBN 9780444513755. http://books.google.com/books?id=F_E9SAe6ny0C&pg=PA13.
- ^ John David Jackson (1999). Classical Electrodynamics (3rd ed.). Wiley. p. 180. ISBN 0-471-30932-X.
- ^ John David Jackson (1999). Classical Electrodynamics (3rd ed.). Wiley. p. 273, eq. (6.150).
- ^ See for example equation (4) in M. Nowakowski, N. G. Kelkar (2005). "Faraday's law in the presence of magnetic monopoles". Europhysics Letters 71 (3): 346. arXiv:physics/0508099. Bibcode 2005EL.....71..346N. doi:10.1209/epl/i2004-10545-2.
- ^ F. Moulin (2001). "Magnetic monopoles and Lorentz force". Il Nuovo Cimento B 116 (8): 869–877. arXiv:math-ph/0203043. Bibcode 2001NCimB.116..869M.
- ^ a b Paul G. Hurray (2010). Maxwell's Equations. p. 22. ISBN 9780470542767. http://books.google.com/books?id=0QsDgdd0MhMC&pg=PA22.